Table of Contents
In the world of automation and smart systems, two key components play pivotal roles: sensors and actuators. These devices are essential to various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. This article will help you understand what sensors and actuators are, their differences, and how they work together to create intelligent systems. We’ll also explore some practical examples of their applications.
What are Sensors?
Sensors are devices that detect or measure physical properties and convert them into signals. These signals can be read by other devices or systems. They serve as the “eyes and ears” of a system, monitoring the environment and providing valuable data. There are various types of sensors, including:
- Temperature sensors: These measure temperature in various environments, such as a room or a machine, and are commonly used in HVAC systems or industrial processes.
- Proximity sensors: Used to detect the presence or absence of nearby objects without making physical contact, they are often employed in robotics, automotive systems, and security applications.
- Pressure sensors: These sensors measure pressure in liquids or gases and find applications in aviation, industrial, and automotive systems.
Read – Need a Sensor? Selection Criteria for Sensors – NerdyElectronics
What are Actuators?
Actuators are devices that convert energy, typically electrical, into mechanical motion or control other devices or systems based on the input received. They serve as the “muscles” of a system, enabling it to perform various actions or tasks. Some common types of actuators include:
- Motors: Electric motors are widely used in robotics, automotive systems, and industrial machinery to provide motion or force.
- Solenoids: These electromagnetic devices convert electrical energy into linear motion and are used in applications like door locks, valves, and relays.
- Servo motors: A special type of motor, servo motors provide precise control of position, speed, or torque, making them ideal for use in robotics and precision machinery.
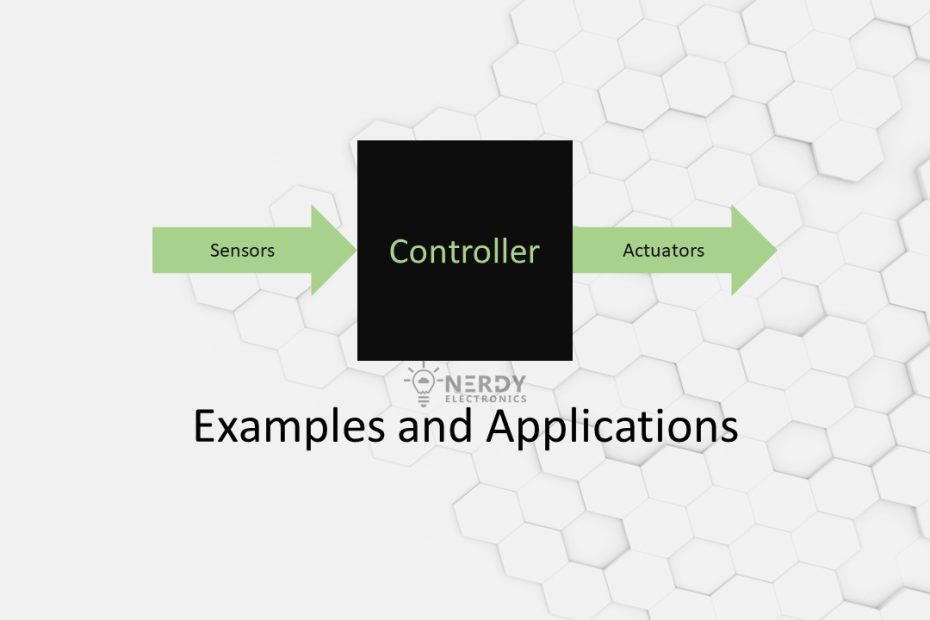
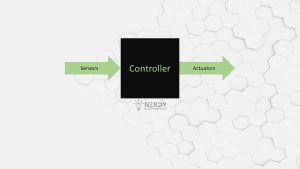
How Sensors and Actuators Work Together
Sensors and actuators work in tandem to create smart systems capable of responding to their environment. The sensor gathers data about a specific physical property, such as temperature or pressure, and transmits this information to a controller. The controller then processes the data, making decisions based on predefined rules or algorithms, and sends commands to the actuator. The actuator then performs the required action, adjusting the system accordingly.
Examples of Sensors and Actuators in Action
- Home automation systems: In a smart thermostat, temperature sensors measure the ambient temperature and send the information to the thermostat controller. Based on the user’s settings, the controller commands an actuator, like a motor, to adjust the HVAC system, maintaining the desired temperature.
- Industrial automation: In an assembly line, proximity sensors can detect the presence of a product on a conveyor belt. If the sensor detects a product, it sends a signal to a controller that, in turn, commands a robotic arm (actuator) to pick up the product and place it in the correct position.
- Automotive systems: Modern cars use a combination of sensors and actuators to maintain optimal engine performance. For example, an oxygen sensor measures the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases, and the engine control unit adjusts the fuel injection rate (actuator) to maintain the ideal air-fuel mixture.
Conclusion
Sensors and actuators are crucial components of modern smart systems, playing a vital role in various applications across industries. By working together, they enable intelligent systems to monitor, analyze, and respond to their environment, enhancing efficiency, safety, and convenience. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative uses of sensors and actuators.
Hi, I’m Vivek, a Senior Embedded Innovation Specialist. I have been working on Embedded Systems and IoT for the past 11 years. I love to share my knowledge and train those who are interested. Nerdyelectronics.com was started out of this interest. You can read my full profile in this link.