Table of Contents
Sets in Python
Welcome! This notebook will teach you about the sets in the Python Programming Language. By the end of this lab, you’ll know the basics set operations in Python, including what it is, operations and logic operations.
Sets
Set Content
A set is a unique collection of objects in Python. You can denote a set with a curly bracket {}. Python will automatically remove duplicate items:
# Create a set
set1 = {"pop", "rock", "soul", "hard rock", "rock", "R&B", "rock", "disco"}
set1
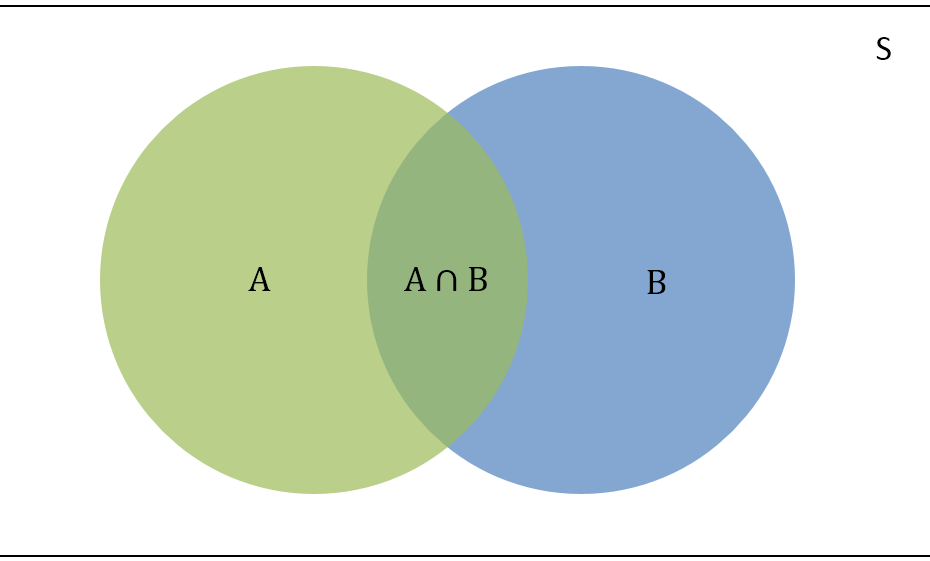
{'R&B', 'disco', 'hard rock', 'pop', 'rock', 'soul'}The process of mapping is illustrated in the figure:
# Convert list to set
album_list = [ "Michael Jackson", "Thriller", 1982, "00:42:19", \
"Pop, Rock, R&B", 46.0, 65, "30-Nov-82", None, 10.0]
album_set = set(album_list)
album_set
{'00:42:19',
10.0,
1982,
'30-Nov-82',
46.0,
65,
'Michael Jackson',
None,
'Pop, Rock, R&B',
'Thriller'}Now let us create a set of genres:
# Convert list to set
music_genres = set(["pop", "pop", "rock", "folk rock", "hard rock", "soul", \
"progressive rock", "soft rock", "R&B", "disco"])
music_genres
{'R&B',
'disco',
'folk rock',
'hard rock',
'pop',
'progressive rock',
'rock',
'soft rock',
'soul'}Set Operations
Let us go over set operations, as these can be used to change the set. Consider the set A:
# Sample set
A = set(["Thriller", "Back in Black", "AC/DC"])
A
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black', 'Thriller'}Add element to set
We can add an element to a set using the add() method:
# Add element to set
A.add("NSYNC")
A
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black', 'NSYNC', 'Thriller'}If we add the same element twice, nothing will happen as there can be no duplicates in a set:
# Try to add duplicate element to the set
A.add("NSYNC")
A
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black', 'NSYNC', 'Thriller'}Remove an element from set
We can remove an item from a set using the remove method:
# Remove the element from set
A.remove("NSYNC")
A
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black', 'Thriller'}Check if the element is in the set
We can verify if an element is in the set using the in command:
# Verify if the element is in the set
"AC/DC" in A
True
Sets Logic Operations
Remember that with sets you can check the difference between sets, as well as the symmetric difference, intersection, and union:
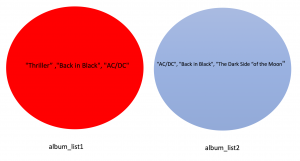
Consider the following two sets:
# Print two sets
album_set1, album_set2
({'AC/DC', 'Back in Black', 'Thriller'},
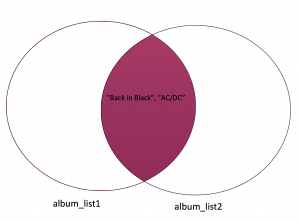
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black', 'The Dark Side of the Moon'})As both sets contain AC/DC and Back in Black we represent these common elements with the intersection of two circles.
# Find the intersections
intersection = album_set1 & album_set2
intersection
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black'}Difference in Sets
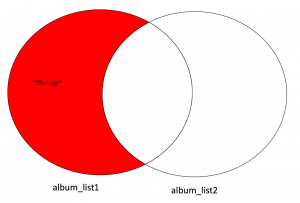
You can find all the elements that are only contained in album_set1 using the difference method:
# Find the difference in set1 but not set2
album_set1.difference(album_set2)
{'Thriller'}You only need to consider elements in album_set1; all the elements in album_set2, including the intersection, are not included.
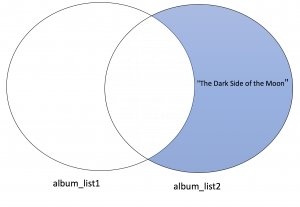
album_set2.difference(album_set1)
{'The Dark Side of the Moon'}# Use intersection method to find the intersection of album_list1 and album_list2
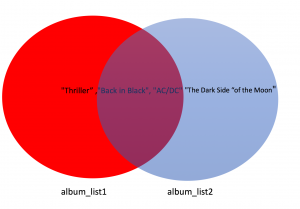
album_set1.intersection(album_set2)
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black'}This corresponds to the intersection of the two circles:
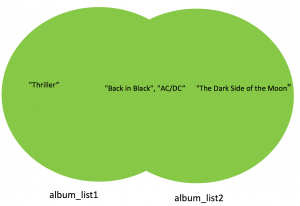
The union corresponds to all the elements in both sets, which is represented by coloring both circles:
# Find the union of two sets
album_set1.union(album_set2)
{'AC/DC', 'Back in Black', 'The Dark Side of the Moon', 'Thriller'}Superset and Subset
And you can check if a set is a superset or subset of another set, respectively, like this:
# Check if superset
set(album_set1).issuperset(album_set2)
False
# Check if subset
set(album_set2).issubset(album_set1)
False
Here is an example where issubset() and issuperset() return true:
# Check if subset
set({"Back in Black", "AC/DC"}).issubset(album_set1)
True
# Check if superset
album_set1.issuperset({"Back in Black", "AC/DC"})
True
Quiz on Sets
Convert the list ['rap','house','electronic music', 'rap'] to a set:
set([‘rap’,’house’,’electronic music’,’rap’])
Consider the list A = [1, 2, 2, 1] and set B = set([1, 2, 2, 1]), does sum(A) = sum(B)
Your answer is below:
A = [1, 2, 2, 1]
B = set([1, 2, 2, 1])
print(“the sum of A is:”, sum(A))
print(“the sum of B is:”, sum(B))
Create a new set album_set3 that is the union of album_set1 and album_set2:
album_set1 = set(["Thriller", 'AC/DC', 'Back in Black'])
album_set2 = set([ "AC/DC", "Back in Black", "The Dark Side of the Moon"])
Your answer is below:
album_set3 = album_set1.union(album_set2)
album_set3
Find out if album_set1 is a subset of album_set3:
Your answer is below:
album_set1.issubset(album_set3)